- 0391-6109928
- 15302105619
- export01@zw-pvp.com
- Language:


Purity:99%
Jiaozuo Zhongwei Special Products Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Zhongwei) is a manufacturer specializing in the production of pharmaceutical excipients and a national high-tech enterprise. The company has an excellent technical, marketing and management team, equipped with a complete set of production and testing equipment; focusing on the research and development, production and sales of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) series products, and is committed to providing high-quality polyvinylpyrrolidone products and solutions to global customers. The company focuses on providing quality assurance, regulatory compliance and technical support services for polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) series products to global customers. With international certification (ISO9001, CEP) and strict quality inspection systems, we ensure that our products meet the pharmacopoeia standards of many countries; through environmental compliance management, we ensure sustainable development. In terms of technical services, relying on the R&D center and expert team, we provide customized solutions from formula optimization, process improvement to on-site support to help customers improve product performance and production efficiency.
| Product Name: | 1-octyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| Synonyms: | N-ethyl pyrrolidone; 1-OCTYLPYRROLIDIN-2-ONE; 1-OCTYL-2-PYRROLIDINONE; 1-N-OCTYL-2-PYRROLIDONE; N-OCTYL PYRROLIDONE; N-OCTYL-2-PYRROLIDONE; 1-octyl-2-pyrrolidinon; 2-Pyrrolidinone,1-octyl-; N-(n-octyl)-2-pyrrolidinone; NOP |
| CAS RN.: | 2687-94-7 |
| Molecular Weight: | 197.3171 |
| Molecular Formula: | C12H23NO |
| Density: | 0.926g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point(℃): | 303.1°C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point(℃): | 129°C |
Synthesis
N-Octyl pyrrolidone was synthesized by 2-pyrrolidone and tetrabutylammonium bromide stirred with adding n-octane chloride for 10 h at 90 °C.
Chemical Properties
Colorless or slightly yellow clear liquid
Uses
N-Octyl pyrrolidone(NOP) is a highly efficient and selective solvent, which can be used in the recovery of organic raw materials, the refining of lubricating oils, and the solvent for polymers and polymerization reactions; It is also widely used in chemical synthesis reactions.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 57, p. 3328, 1992 DOI: 10.1021/jo00038a019
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 59, p. 6378, 1994 DOI: 10.1021/jo00100a046
General Description
1-Octyl-2-pyrrolidone is a permeation enhancer and its effect in transport of steroidal permeants across hairless mouse skin was investigated via a parallel pathway skin model.
Flammability and Explosibility
Nonflammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Asevere skin and eye irritant. A corrosive. Combustibleliquid. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumesof NOx.
InChI:InChI=1/C12H23NO/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-10-13-11-8-9-12(13)14/h2-11H2,1H3
The selective N-alkylation of amides (cyclic or acyclic) under hydrogen is reported using aldehydes or ketones as alkylating agents and Pd/C/Na2SO4 as catalyst. Good isolated yields are obtained (81% to 98%).
Several N-substituted azacyclopentanones were synthesized and evaluated as repellents for the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Several of these compounds were more effective in our test system than were the standard repellents, N,N-dimethyl-m-toluamide and butopyranoxyl.
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of N-substituted lactams by reaction of a lactam, which is unsubstituted on the nitrogen, with an organic halide in the presence of at least one solid-liquid phase transfer catalyst, such as a quaternary ammonium salt, and of at least one solid inorganic base, such as an alkali metal hydroxide, and in the absence of solvent. By this process, N-substituted lactams are obtained with good yields and high purity. The absence of solvent makes possible a considerable gain in productivity and an improvement in safety and in regard for the environment.
Different amides have been selectively mono-N-alkylated using catalytic heterogeneous palladium and carbonyl compounds as alkylating agents. The same salt free method has been applied to the synthesis of ethers from alcohols. Reaction parameters have been studied in detail and a mechanism is proposed.
Crystallization of active material in spraying of an aqueous solution of certain specified fungicides is retarded by incorporation therein of an N-alkyl-lactam of the formula STR1 in which R represents alkyl having 6 to 18 carbon atoms and n represents the numbers 3, 4 or 5.
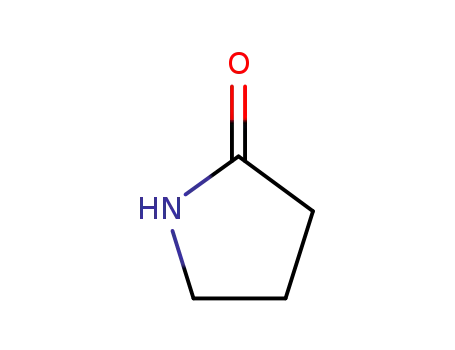
2-pyrrolidinon
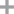
Octanal

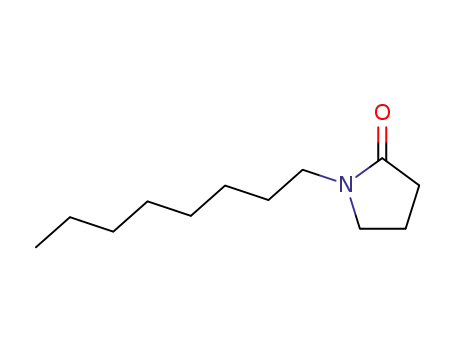
1-n-octyl-2-pyrrolidinone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen; sodium sulfate; palladium on activated charcoal; In ethyl acetate; at 100 ℃; for 4h; under 30002.4 Torr;
|
93% |
|
With hydrogen; sodium sulfate; palladium on activated charcoal; In ethyl acetate; at 100 ℃; for 4h; under 30002.4 Torr;
|
93% |

2-pyrrolidinon

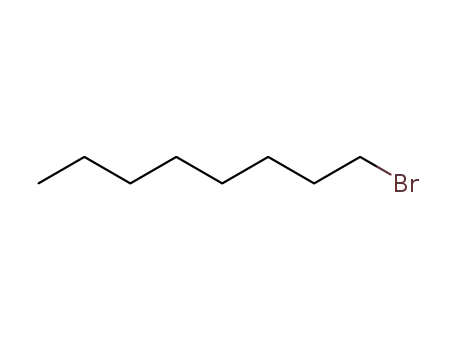
1-bromo-octane


1-n-octyl-2-pyrrolidinone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium tert-butylate; In dimethyl sulfoxide;
|
85% |
|
With NaH; In toluene; Petroleum ether;
|

2-pyrrolidinon

1-bromo-octane

Octanal

n-chlorooctane
sodium lauroyloxybenzenesulfonate

2-pyrrolidinon

1-bromo-octane

nonanoyloxybenzenesulfonate sodium